Tuschl Lab
Inherited manganese transporter defects
Tuschl Lab
Inherited manganese transporter defects
Inherited manganese transporter defects
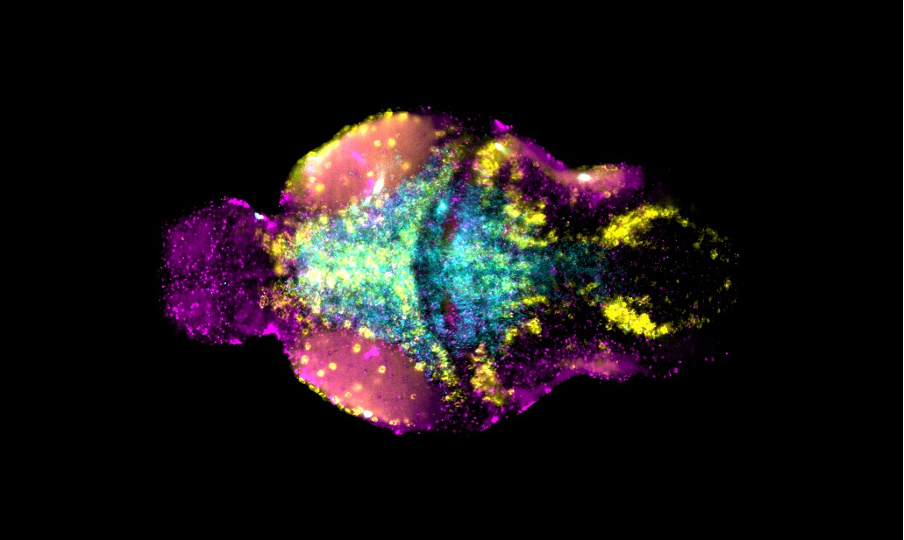
Manganese is an essential trace metal and critical for brain physiology and development. However, excess manganese is neurotoxic leading to dystonia-parkinsonism, psychiatric and intellectual disability.
Our research has identified two manganese transporter defects associated with manganese neurotoxicity – hypermanganesaemia with dystonia 1 (HMNDYT1) and 2 (HMNDYT2). They are caused by loss-of-function mutations in SLC30A10 and SLC39A14, respectively, that encode manganese transporters that act in conjunction to mediate metal excretion. Manganese deposition in the brain leads to progressive, childhood-onset dystonia-parkinsonism associated with significant disability and premature death.
MRI brain
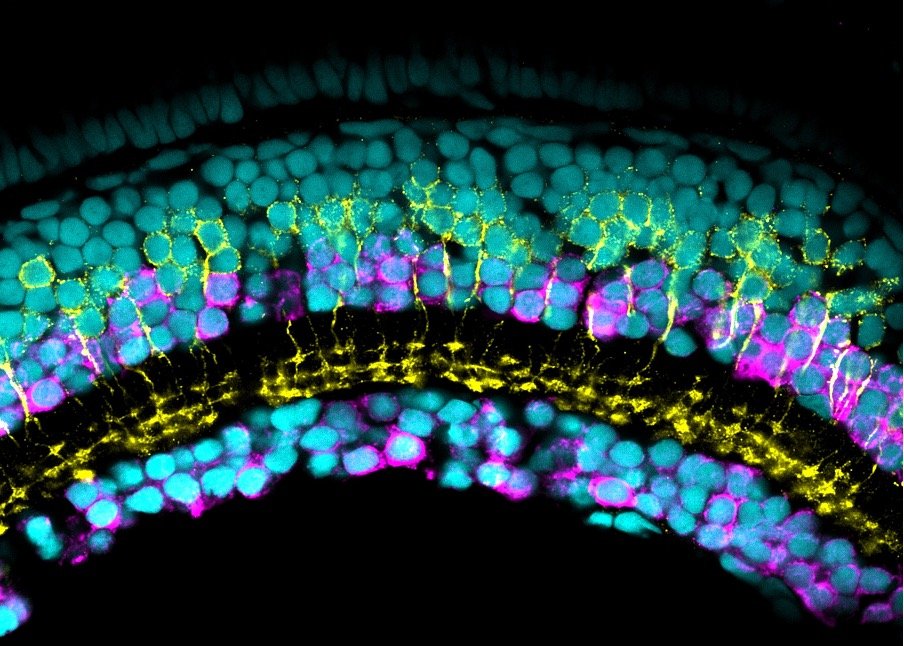
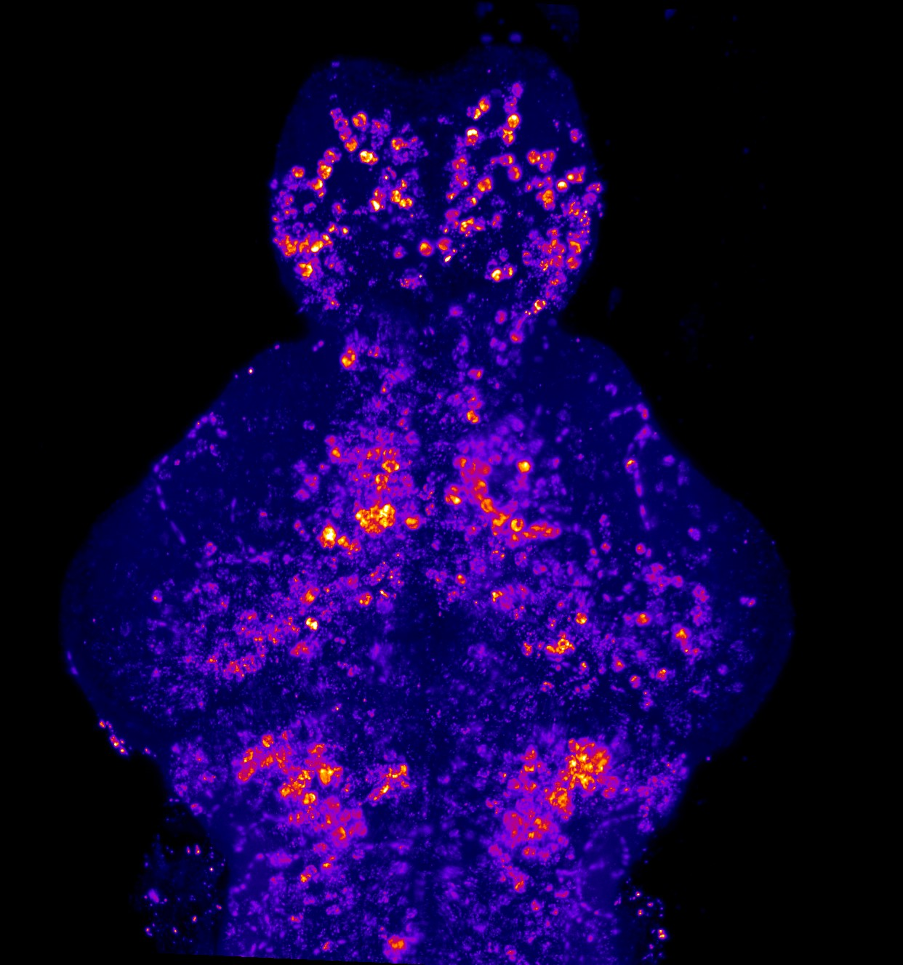
Our lab uses manganese transporter mutant zebrafish as models for manganese overload/deficiency in order to dissect how metal dyshomeostasis disrupts neurons, synapses and circuit function with the view to identifying new therapeutic targets. In addition, we are working to develop novel therapeutic approaches to improve treatments for disorders associated with Mn neurotoxicity.
VITAMIN B6 DEPENDENT EPILEPSY
Vitamin B6, normally present in our diet, is critical for brain function. Children with inherited disorders that lead to severe deficiency of B6 suffer from seizures, delayed neurodevelopment and brain malformations.
In collaboration with Prof Philippa Mills (UCL GOS ICH) and Dr Richard Rosch (Imaging Neuroscience) we are trying to better understand the consequences of B6 deficiency on brain function. Using zebrafish disease models that recapitulate the seizure disorders observed in affected children, we will investigate how imbalance of B6 impairs the chemical messengers ('neurotransmitters') in the brain that are required to transmit messages from a nerve cell to a target cell. Thereby, we hope to identify novel therapeutic targets that can be translated into new treatments for affected children to prevent disability and improve children’s quality of life.
Tuschl Lab News
follow us on twitter: @KarinTuschl

People
People
about me
I am an MRC Clinician Scientist Fellow at the UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health and consultant in paediatric metabolic medicine at Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children. I specialise in genetic disorders associated with metal dyshomeostasis. My lab is part of Zebrafish research at UCL. We use manganese transporter mutant zebrafish as models for manganese overload/deficiency in order to dissect how metal dyshomeostasis disrupts neurons, synapses and circuit function with the view to identifying new therapeutic targets.
GRANTS
· 2023 UCL Therapeutic Acceleration Support Fund Rare Diseases Call
· 2023 Action Medical Research Project Grant
· 2022 NIHR GOSH BRC for your Junior Faculty Consumables
· 2021 UCL Small Molecules TIN Pilot Data Scheme
· 2021 UCL Accelerate Innovation Team Challenge – Team AccessBrain
2021 MRC Clinician Scientist Fellowship
2017 GOSHCC Clinical Research Starter Grant
2017 Starter Grant for Clinical Lecturers, Academy of Medical Sciences
2016 UCL Neuroscience ZNZ Collaboration
2012 Action Medical Research – Research Training Fellowship
Lab Members
Past Lab Members
Artur Fernandes – Postdoc
Rebecca Wills – MSc GHD student
Aanandita Kothurkar – MSc GHD student
Anabel Alba González - Visiting PhD Student
Valeria Nikolaenko- Postdoc
Collaborators
Prof Stephen Wilson, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, UCL
Prof Ahad Rahim, School of Pharmacy, UCL
Prof John Spencer & Dr George Kostakis, Department of Chemistry, University of Sussex
Prof Philip Blower, Department of Imaging Chemistry and Biology, KCL
Prof Philippa Mills, UCL GOS Institute of Child Health
Dr Richard Rosch, Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, UCL
Dr Ryan Macdonald, Institute of Ophthalmology, UCL
Prof Thomas Bartnikas, Brown University, US
Prof Giulio Superti-Furga, Centre for Molecular Medicine, Vienna, Austria
Dr Mónica Folgueira, Centro Interdisciplinar de Química y Biología, (CICA), University of A Coruña, Spain
Lab Photos

Publications
Publications
Selected publications
Alba-González, A.; Dragomir, E.I.; Haghdousti, G.; Yáñez, J.; Dadswell, C.; González-Méndez, R.; Wilson, S.W.; Tuschl, K.; Folgueira, M. Manganese Overexposure Alters Neurogranin Expression and Causes Behavioral Deficits in Larval Zebrafish.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094933
Gurung S, Karamched S, Perocheau D, Seunarine KK, Baldwin T, Alrashidi H, Touramanidou L, Duff C, Elkhateeb N, Stepien KM, Sharma R, Morris A, Hartley T, Crowther L, Grunewald S, Cleary M, Mundy H, Chakrapani A, Batzios S, Davison J, Footitt E, Tuschl K, Lachmann R, Murphy E, Santra S, Uudelepp ML, Yeo M, Finn PF, Cavedon A, Siddiqui S, Rice L, Martini PGV, Frassetto A, Heales S, Mills PB, Gissen P, Clayden JD, Clark CA, Eaton S, Kalber TL, Baruteau J.
The incidence of movement disorder increases with age and contrasts with subtle and limited neuroimaging abnormalities in argininosuccinic aciduria.
J Inherit Metab Dis. 2023. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12691.
Messina M, Manea E, Cullup T, Tuschl K, Batzios S.
Hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome 3: Cerebrospinal fluid abnormalities and correction with pyridoxine and Folinic acid.
JIMD Rep. 2022 Nov 22;64(1):42-52.
Tuschl K, White RJ, Trivedi C, Valdivia LE, Niklaus S, Bianco IH, Dadswell C, González-Méndez R, Sealy IM, Neuhauss SCF, Houart C, Rihel J, Wilson SW, Busch-Nentwich EM.
Loss of slc39a14 causes simultaneous manganese hypersensitivity and deficiency in zebrafish.
Dis Model Mech. 2022. doi: 10.1242/dmm.044594.
Tuschl K, Taylor CA, Nicolai MM, Bornhorst J, Gubert P, Varão AM, Aschner M, Smith DR, Mukhopadhyay S.
Maintaining Translational Relevance in Animal Models of Manganese Neurotoxicity.
J Nutr. 2020;150:1360-1369.
Tuschl K, White RJ, Valdivia LE, Niklaus S, Bianco IH, Sealy IM, Neuhauss SCF, Houart C, Wilson SW, Busch-Nentwich EM.
Loss of slc39a14 causes simultaneous manganese deficiency and hypersensitivity in zebrafish.
doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.31.921130
Tuschl K, Yapici Z, Eraksoy M.
Hypermanganesemia with dystonia 1 – a novel mutation and response to iron supplementation.
Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2019. 7:94-96.
Anagianni S, Tuschl K.
Genetic Disorders of Manganese Metabolism.
Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019. 19:33.
Baguña Torres J, Yu Z, Bordoloi J, Sunassee K, Smith D, Smith C, Chen O, Purchase R, Tuschl K, Spencer J, Platt F, Blower PJ.
Imaging of changes in copper trafficking and redistribution in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick C disease using positron emission tomography.
Biometals. 2019. 32:293-306.
Rodan LH, Hauptman M, D'Gama AM, Qualls AE, Cao S, Tuschl K, et al.
Novel founder intronic variant in SLC39A14 in two families causing Manganism and potential treatment strategies.
Mol Genet Metab. 2018. 124:161-167.
Tuschl K, Gregory A, Meyer E, Clayton PT, Hayflick SJ, Mills PB, Kurian MA.
SLC39A14 Deficiency.
In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K, Amemiya A, editors.
GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2018.
Tuschl K, Meyer E, Valdivia LE, Zhao N, Dadswell C, Abdul-Sada A, Hung CY, Simpson MA, Chong WK, Jacques TS, Woltjer RL, Eaton S, Gregory A, Sanford L, Kara E, Houlden H, Cuno SM, Prokisch H, Valletta L, Tiranti V, Younis R, Maher ER, Spencer J, Straatman-Iwanowska A, Gissen P, Selim LA, Pintos-Morell G, Coroleu-Lletget W, Mohammad SS, Yoganathan S, Dale RC, Thomas M, Rihel J, Bodamer OA, Enns CA, Hayflick SJ, Clayton PT, Mills PB, Kurian MA, Wilson SW.
Mutations in SLC39A14 disrupt manganese homeostasis and cause childhood-onset parkinsonism-dystonia.
Nat Comms. 2016. 7:11601
Tuschl K, Mills PB, Clayton PT.
Manganese and the brain.
Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013. 110:277-312
Tuschl K, Clayton PT, Gospe SM, Mills PB.
Dystonia/Parkinsonism, Hypermanganesemia, Polycythemia, and Chronic Liver Disease. In: Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Stephens K, Adam MP, editors.
GeneReviews™. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 2012 (updated 2014)
Tuschl K, Stamelou M, Chong WK, Burroughs AK et al.
Dystonia with brain manganese accumulation resulting from SLC30A10 mutations: a new treatable disorder.
Mov Disord. 2012. 27:1317-1322
Tuschl K, Clayton PT, Gospe SM, Shamshad G, et al.
Syndrome of hepatic cirrhosis, dystonia, polycythaemia and hypermanganesaemia – caused by mutations in SLC30A10, a manganese transporter in man.
Am J Hum Genet. 2012. 90:457-466

Funding
Funding
Our research is generously funded by:

Contact
Contact
Contact
For all inquiries please email: k.tuschl@ucl.ac.uk
UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health
30 Guilford Street
London WC1N 1EH
websites
GOS ICH
Genetics and Genomic Medicine at GOS ICH
follow us on X: @KarinTuschl