MOVIES
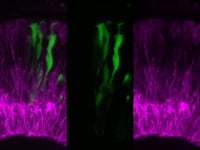
In vivo time lapse of Notch activity within clones in the embryonic retina. Time-lapse confocal imaging of mosaic retinas with Tg(Tp1:Venus) (green)-labeled clones within host retinas where many retinal neurons are labeled by Tg(ath5:gapRFP)(magenta). The cell that will be specified to the glial fate turns on Notch signalling (green) very high before undergoing morphogenesis. Images are of maximum-intensity projections of five confocal slices from time-lapse confocal microscopy using a laser-scanning confocal microscope. Time is shown in hours:minutes. Imaging begins at ∼38 hpf and frames were taken every 15 min for ∼24 h. From DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201503115.
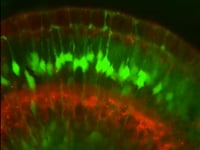
Time-lapse confocal imaging of retinas with all MG labelled with Tg(gfap:gfp) (green) and many retinal neurons are labelled by Tg(ath5:gapRFP)(red). Images are of maximum-intensity projections of five confocal slices from time-lapse confocal microscopy using a laser-scanning confocal microscope. Imaging begins at ∼60 hpf and frames were taken every 15 min for ∼24 h.
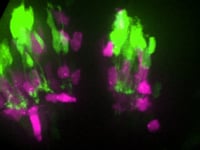
Time-lapse spinning disk confocal imaging of mosaic retinas containing vsx1:GFP-expressing bipolar cell neurons (green) and ptf1a:DsRed-expressing amacrine cell neurons (magenta) in an unlabeled host retina. At the onset of the imaging session, ptf1a:DsRed expressing neurons have migrated to their position in the retina before bipolar cell axons stratify within the ptf1a-expressing cells (arrowheads) to form synaptic connections. Images are confocal reconstructions. Time shown in hr:min. Imaging begins at ∼40 hpf. From DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.01.020.
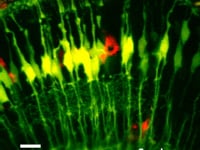
A maximum intensity projection time-lapse movie showing Müller cells (in green) and Microglia (in red) in a 4 day post fertilisation zebrafish retina. Targeted ablation with a pulsed NIR laser allows the triggering of single cell death and the glial response to clean up the debris. Movie from continual imaging with 2-photon excitation.

To determine if a fish can see, or how well they can see, we use innate visual behaviours like the optokinetic response. This embryonic zebrafish is being shown different patterns rotating around it and responding by following them with its’ eyes. We can measure this movement relative to each stimuli and determine their ability to see.

